Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that manifests as impaired communication and social skills, unusual responses to sensory information, lack of attentiveness, and restricted repetitive sensory behavior. AI has shown promising results in aiding the diagnosis, assessment, and personalized treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
This research has been carried out in NUST-COVENTRY Human-Robot Interaction Lab (NC-HRI) at School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering (SMME) NUST.
The project aims at developing a Robot-Inspired Web-Assisted Adaptive Autism Therapy called RIWA3T to help children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) improve their ability to engage in Joint Attention (JA) and imitation skills. This web-based application combined the benefits of Robot-Assisted Therapies (RATs) with Computer-Assisted Therapies (CATs) using robot avatars and a web-based platform. RIWA3T offers personalized content and incorporates AI-based gaze and pose detection technology to ensure accuracy and reduce human error and bias.
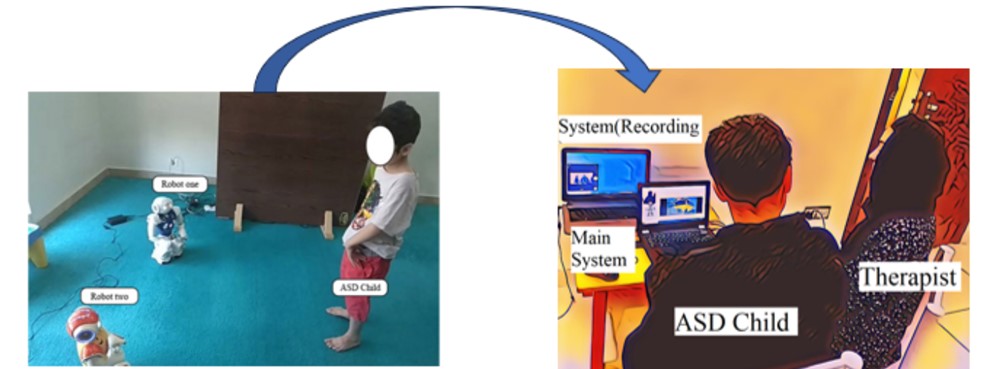
The application focuses on developing an affordable, accessible, and adaptive autism therapy solution that uses AI to predict the performance of autistic children and provide customized therapy accordingly. The solution will offer progress monitoring, guidance, and support for carers of autistic children. It will be built around standard guidelines of Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS), use a robot avatar, and have multi-level adaptability. The goal is to provide a one-stop treatment solution based on robotic interventions that can be easily accessed and utilized by individuals with autism in Pakistan and other countries.
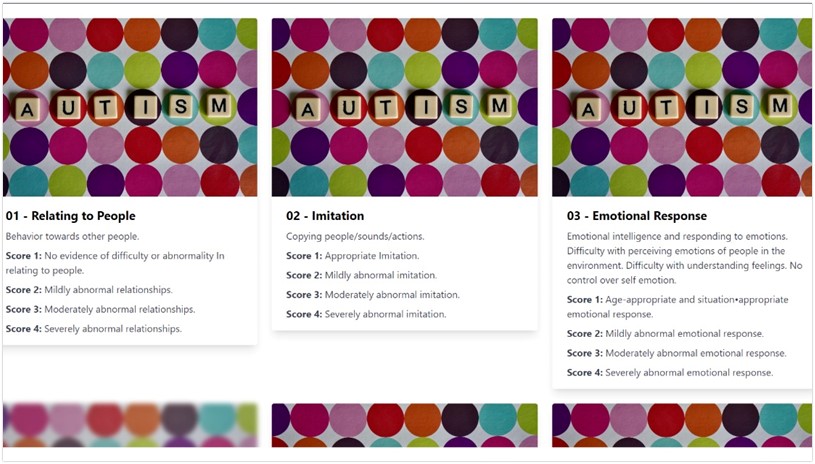
We used advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques and methods for gaze detection and pose estimation. This automation eliminates human errors and biases, ensuring accurate results. The joint attention module uses cues from the robot to assess how well a child follows the robot’s gaze, and the imitation module evaluates how accurately a child imitates the robot’s actions. The therapy adapts based on the child’s progress.
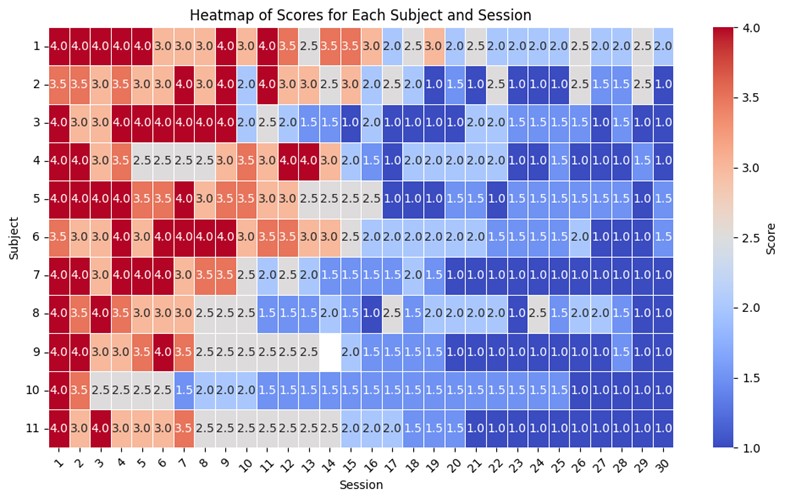
The pilot run of this study has been tested on 11 ASD children over eight months, including 660 experimental trials, 110 familiarization sessions, and 110 follow-up sessions at Primal Support, E-11, Islamabad, Pakistan. The therapy significantly improved the children’s Joint Attention and imitation skills. We measured this improvement using CARS scores, and the results showed marked reductions, particularly in JA and imitation. The statistical tests show significant differences between the first and second halves of therapy sessions. In summary, our study demonstrates the positive impact of RIWA3T on improving the social and imitation skills of children with ASD.
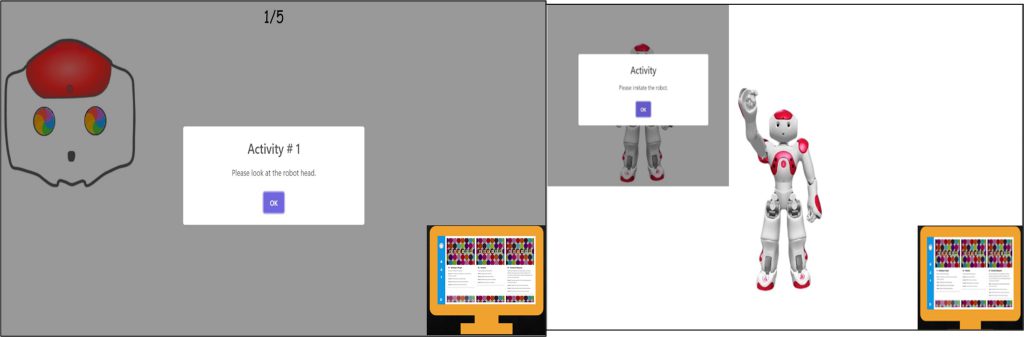
A user-friendly web application has been created, which interacts with the ASD child based on his/her preference. Following are the key-features offered by RIWA3T:
- Prioritizes inclusivity, caters to the unique needs of children with ASD.
- Comprehensive visual, auditory, and motor support.
- Reduced cognitive load by offering simplified activities broken down into manageable sub-tasks.
- Personalized content delivery.
- Progress tracking is provided for therapists, parents, and caregivers.
- Integrated rewards provide incentives and positive reinforcement.

In future, this project will further explore the use of Generative AI in the context of autism spectrum disorder to create customized interventions in order to cater individual needs and preferences along with assessments for individuals with ASD. The potential benefit of this algorithm will be around allowing timely interventions and improved outcomes using personalized nature of the interventions that will cater to the specific requirements of individual, optimizing the effectiveness of treatment plans.
Video demonstration of Robot Inspired Web Therapy for ASD Treatment
The author is Assistant Professor and Director of NUST Coventry Human-Robot Interaction Lab (NC-HRI) at School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering (SMME), and PI of Intelligent Field Robotics Lab (IFRL), National Center of Artificial Intelligence (NCAI), National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST). She can be reached at sarababer@smme.nust.edu.pk.
Research Profile: https://shorturl.at/lnuX5

![]()