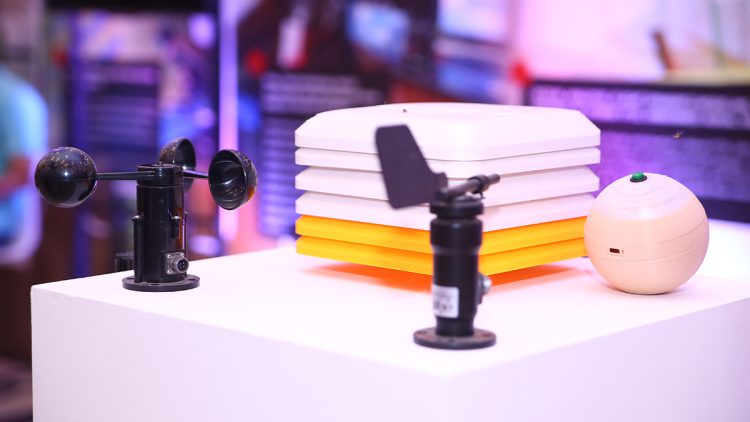
Solar-powered IoT-based weather station is a device that uses solar energy and internet of things (IoT) technology to gather and transmit data about weather conditions such as temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind speed, and direction. The device consists of various sensors that capture these parameters and then transmit the information to a central server, which can then be accessed by the user via the internet.
Having a weather station is important because it provides real-time and accurate weather data that can be used for various purposes such as agricultural planning, disaster management, aviation, and transportation. The weather station can also be used to monitor environmental conditions for scientific research and weather forecasting.
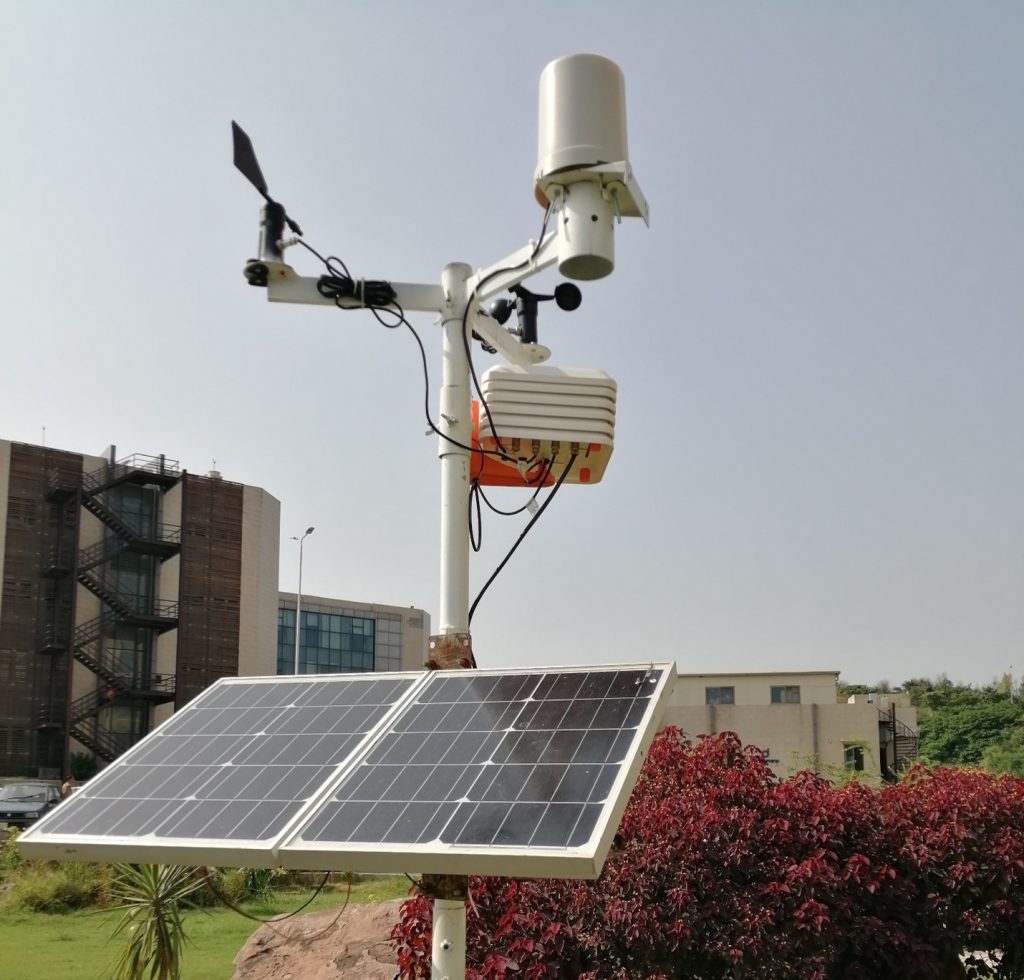

Using solar power to run the weather station has several benefits. First, it is an eco-friendly and sustainable solution, as it eliminates the need for traditional electricity sources that emit harmful gases. Second, it reduces the cost of operating the device, as it requires no external power source, and can operate independently.
IoT technology also brings several benefits to the weather station. It allows for remote monitoring and control of the device, which can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. IoT technology also enables the device to communicate with other connected devices, such as smartphones or computers, to provide users with alerts and notifications about changes in weather conditions. This helps users make informed decisions about their activities and plans.
Solar-powered IoT-based weather station is an important device that provides real-time and accurate weather data. By using solar power and IoT technology, it is a sustainable and cost-effective solution that can be remotely monitored and controlled, bringing several benefits to its users.
Main Components of Weather Station
To build a solar-powered IoT-based weather station, the following components are required:
- Solar panel: It converts solar energy into electrical energy to power the weather station.
- Microcontroller: It controls and manages the different sensors in the weather station and sends data to the central server.
- Sensors: These include temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind speed, and direction sensors, Gas sensors, Rainfall detection and Light Intensity which measure weather parameters.
- Wireless module: It enables communication between the weather station and the central server.
- Battery: It stores energy generated by the solar panel and provides power when there is no sunlight.
- Enclosure: It protects the electronic components of the weather station from weather elements.
Each component plays a crucial role in the functionality of the weather station. The solar panel and battery are responsible for providing sustainable power to the device, while the microcontroller manages and coordinates the sensors’ data. The sensors capture the different weather parameters, and the wireless module transmits the data to the central server. The enclosure protects the electronic components from damage caused by weather elements. The combination of all these components creates a comprehensive weather monitoring system that can provide accurate and real-time data.
How it works
The weather station collects data through the different sensors installed within the device. These sensors measure various weather parameters, such as temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind speed, and direction. The microcontroller in the weather station coordinates and manages the sensors, collects the data, and sends it to the wireless module. The wireless module then transmits the data to the central server, which can be accessed remotely using an internet connection.
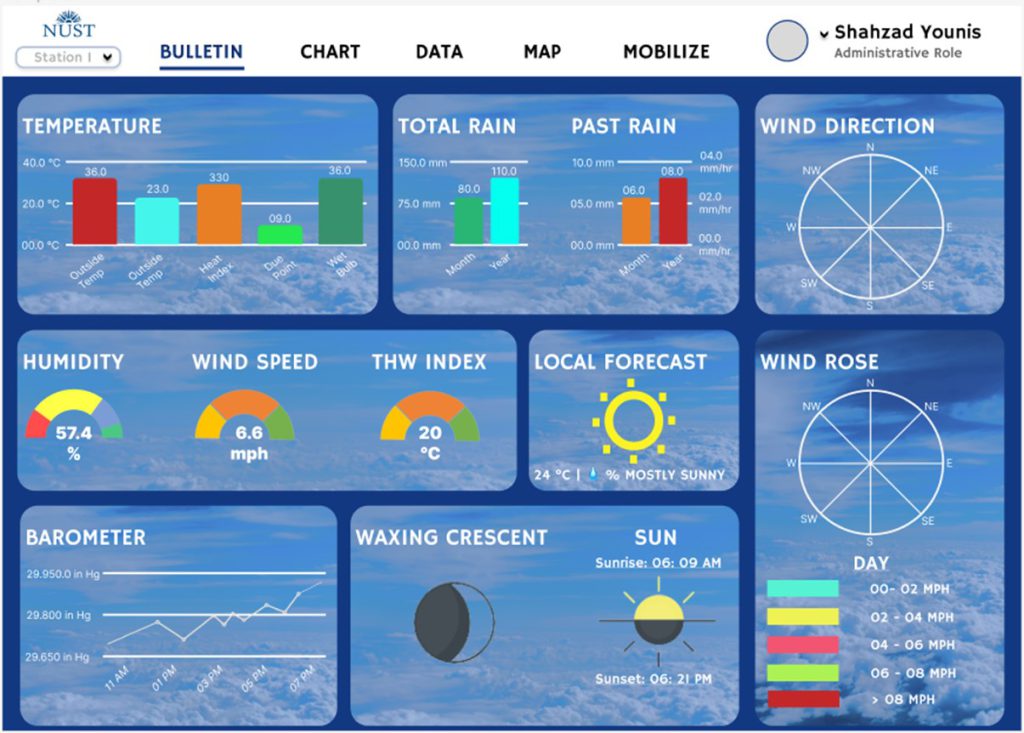
Solar power is used to power the weather station by converting solar energy into electrical energy through the solar panel. The energy generated is used to power the microcontroller, sensors, and wireless module. Any excess energy is stored in the battery, which provides power when there is no sunlight. The use of solar power makes the weather station sustainable, eco-friendly, and cost-effective, as it eliminates the need for external power sources that emit harmful gases and require regular maintenance.
Advantages of a solar-powered IoT-based weather station
There are several advantages to using a solar-powered IoT-based weather station. Firstly, the use of solar power makes the device environmentally friendly and sustainable, as it eliminates the need for traditional electricity sources that emit harmful gases. This makes the weather station a cost-effective and low-maintenance solution for long-term weather monitoring.
Secondly, IoT technology improves the functionality of the weather station by enabling remote monitoring and control of the device. Users can access real-time weather data from anywhere, allowing for efficient and informed decision-making. The integration of other devices, such as smartphones or computers, also enables users to receive alerts and notifications about changes in weather conditions, enhancing the weather station’s usefulness.
Thirdly, having a weather station that is both solar-powered and IoT-based provides several advantages. The device is self-sufficient, requiring no external power source, and can operate independently. It also provides accurate and reliable data that can be used for various purposes, such as agricultural planning, disaster management, and scientific research. The combination of solar power and IoT technology makes the weather station a cost-effective and efficient solution for long-term weather monitoring.
Solar-powered IoT-based weather station provides several advantages, including environmental sustainability, remote monitoring and control, and cost-effectiveness. The device’s self-sufficiency and accurate data make it a useful tool for various applications, making it an excellent investment for long-term weather monitoring.
Applications of a solar-powered IoT-based weather station
Weather station has various applications in different industries. The data collected by the device can be used for:
- Agriculture: Farmers can use the weather station’s data to plan crop planting and irrigation schedules. Accurate weather data can also help farmers predict potential crop diseases, pests, and other hazards.
- Aviation: Weather plays a crucial role in aviation, and the weather station’s data can provide pilots with critical information about wind speed, direction, and turbulence. This information can help pilots make informed decisions about flight paths, altitude, and landing approaches.
- Construction: Weather conditions can impact construction projects, and the weather station’s data can help contractors plan construction schedules and prevent weather-related project delays.
- Disaster management: The weather station’s data can provide early warning signs of potential natural disasters, such as hurricanes, floods, and tornadoes. The data can be used to issue timely alerts and evacuation orders, potentially saving lives and minimizing damage.
- Scientific research: Weather data collected by the weather station can be used in various scientific research fields, including meteorology, climate studies, and environmental research.
The data collected by the weather station can also be used to create weather forecasts, which are essential for many industries, including transportation, tourism, and event planning. By providing accurate and real-time weather data, a solar-powered IoT-based weather station can help businesses and industries make informed decisions, ultimately increasing efficiency and productivity.
Summary
In summary, a solar-powered IoT-based weather station provides many benefits, including sustainability, remote monitoring, cost-effectiveness, and accuracy. This technology has the potential to impact society and the environment positively by providing critical weather data for various industries and improving decision-making processes. The future of solar-powered IoT-based weather stations is promising, as advancements in technology will continue to improve their efficiency and functionality.
The author is Tenured Professor at School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST). He can be reached at muhammad.shahzad@seecs.edu.pk.
Research Profile: https://bit.ly/42i6vlQ

![]()





