The significance of power transmission at high voltages was realized just after the few years of invention of first ever successful power system. This was the famous “War of Currents” era of Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla between late 1880s and early 1890s. The first power system started from 110 volts lightning 3000 lamps having 59 customers. Today’s modern world is ready to evident the power transmission at 1.1 Mega volts (10, 000 times of the first power system) in near future. In our country, the highest AC transmission voltage is 500 kV (AC) and recently on September 01, 2021 first ever national DC transmission line of ± 660 kV has been made operational from Matiari to Lahore. The demand by increased population and industrialization and vogue of engineers and scientists are ever increasing facts that will induce the need of power transmission at higher and higher voltages. However, it is as complex and difficult to implement; as easy to write.
The significance of power transmission at high voltages was realized just after the few years of invention of first ever successful power system. This was the famous “War of Currents” era of Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla between late 1880s and early 1890s. The first power system started from 110 volts lightning 3000 lamps having 59 customers. Today’s modern world is ready to evident the power transmission at 1.1 Mega volts (10, 000 times of the first power system) in near future. In our country, the highest AC transmission voltage is 500 kV (AC) and recently on September 01, 2021 first ever national DC transmission line of ± 660 kV has been made operational from Matiari to Lahore. The demand by increased population and industrialization and vogue of engineers and scientists are ever increasing facts that will induce the need of power transmission at higher and higher voltages. However, it is as complex and difficult to implement; as easy to write.
The most challenging tasks associated with expected and unexpected high voltages are safety, insulation of all power apparatus and power lines, earthing mechanisms, measurement, control etc. These areas need to be researched on national level not only to achieve reliable power transmission but also for the safety and protection of human, environment and all power apparatus. Due to crisis for more than a decade in energy sector and power generation in Pakistan; research cannot be carried out by national power companies in the high voltage engineering field. Keeping in view, national level problems and modern challenges in the high voltages there was an urge to take initiative by potential national academia. NUST being pioneer in many fields has decided to step forward in this area as well.
In April, 2018 the project of development of High Voltage Laboratory NUST (HVLN) started with the aim to have national level facility for helping researchers and national industry through extensive R&D work. To achieve these goals a dedicated separate building with covering area of 500 m2 (20 ×25) and 7.5 meters height was approved and procurement of high standard, reliable international equipment was initiated. High Voltage Laboratory, USPCAS-E, NUST has been recently established and commissioned in August 2021. The building is designed and implemented as per International Electro-technical Commission (IEC) standards i.e. IEC 61936-1:2021, IEC60364-1 and IEC 61000-4-23
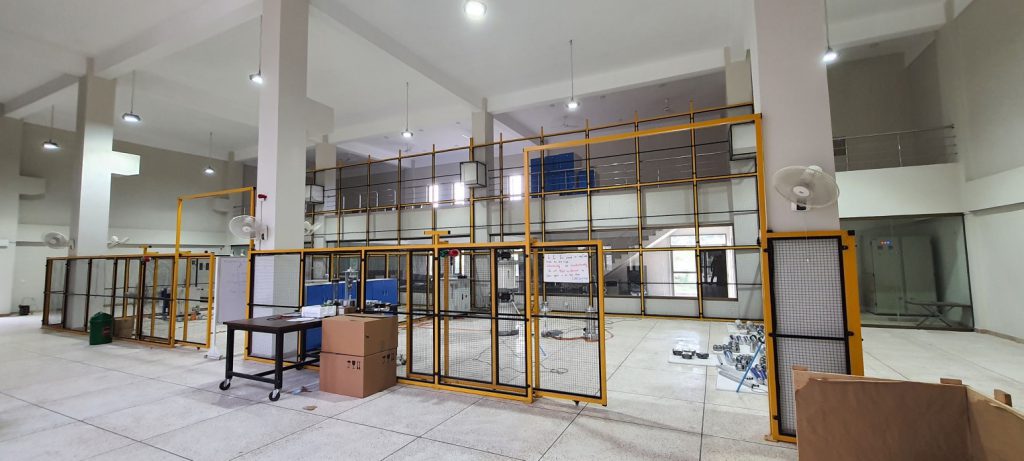

In order to achieve the objectives of highest reliability, accuracy and safety; leading equipment from prestigious companies (Haefely, Hipotronics and Tettex) were procured and recently installed and commissioned as per international standards by team consisted of members from USPCAS-E , NUST (Pakistan), HAEFELY AG- (Switzerland) and RASTEK Technologies (Pakistan).
HVLN contains the following equipment:
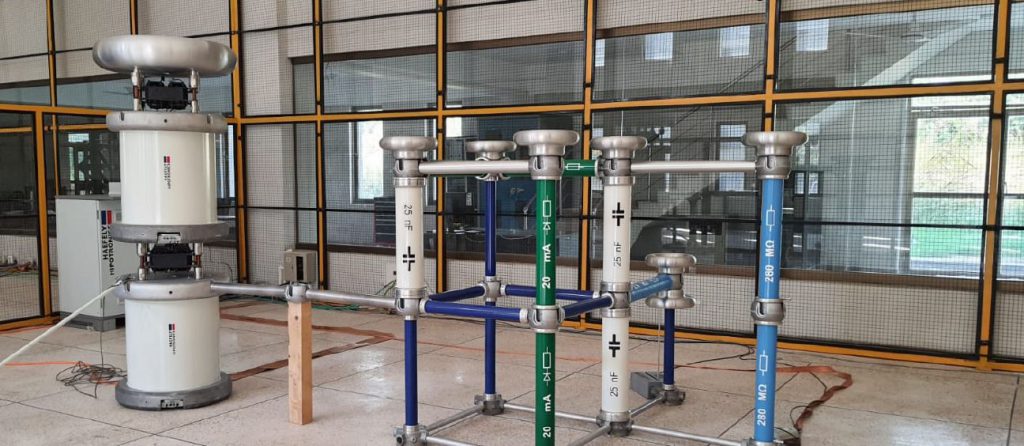
- High Voltage Impulse Generator (400 kV and 20 kJ/ 200 kV and 40 kJ)
⇒ It is four stages system used for lighting impulse testing of power apparatus. - Modular KIT of variable High Voltage AC Generator (up to 200 kV AC voltage)
⇒ It is high end system that can be used in different multipurpose AC destructive and nondestructive testings. - Modular KIT of variable High Voltage DC Generator (can generate up to ±280 kV DC voltage)
⇒ It is high end system that can be used in different multipurpose DC destructive and nondestructive testings. - Partial Discharge Analyzing System
⇒ This setup is capable to analyze AC partial discharges in low and high frequency range with variable high voltage input. - AC Solid Dielectric Breakdown Tester with up to 75 kV (R.M.S) Breakdown Voltage
⇒ A very accurate dedicated unit designed according to ASTM D-149 standard for failure analysis and life estimation of high voltage insulators. - AC Liquid Dielectric Breakdown Tester with up to 60 kV (R.M.S) Breakdown Voltage
⇒ This is also dedicated setup designed according to ASTM D1816 – 12 (2019) for failure analyses and life estimation of oils and other insulating liquids. - Dielectric Properties Analyzer-I
⇒ Using this equipment different dielectric property of solids and liquids can be tested at high temperatures and low frequency. - Dielectric Properties Analyzer-II
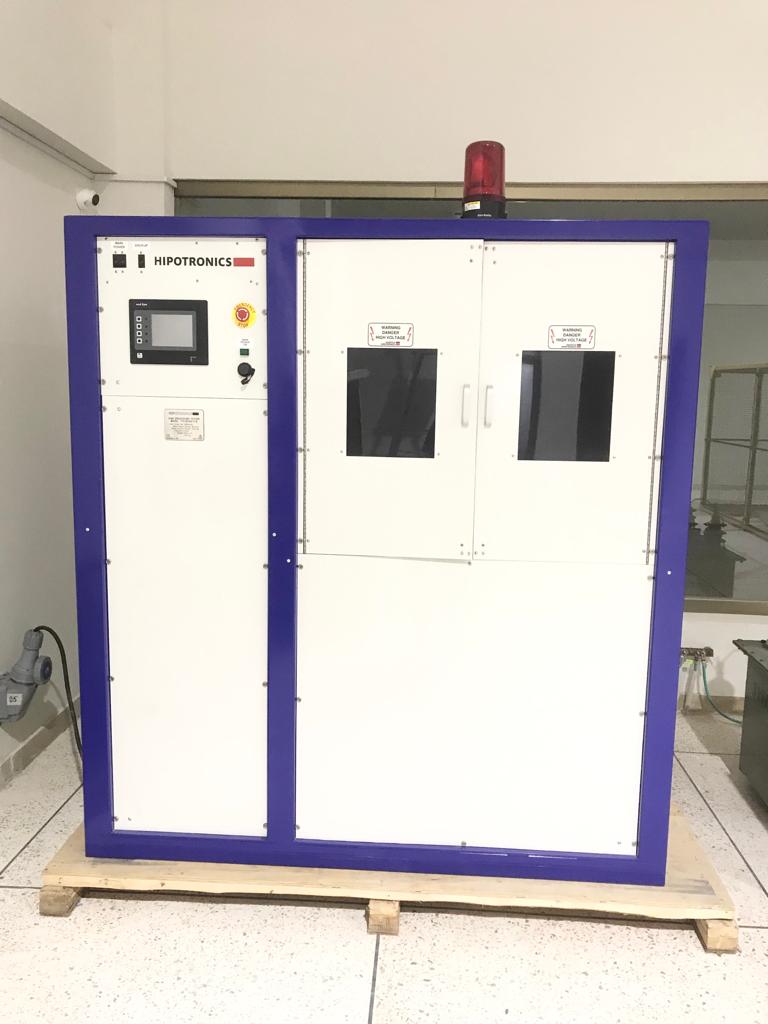
⇒ Using this equipment different dielectric property of solids and liquids can be tested at high temperatures and low frequency. - AC / DC (5 kV/6 kV) Hipot Tester with Mega Ohm meter)
⇒ It is used for testing quality of insulation. - 40kV DC or 28kV AC Direct Measurement System
⇒ It is portable setup that can be used in field for direct measurement of voltage in the specified range. - Earth Ground Tester
⇒ The earth ground tester is to periodically check the grounding system confirm the high voltage grounding (above 270 kV) as per standard. - Programmable Temperature and Humidity Chamber by UTSTESTER
⇒ It can be used for qualitative and quantitative analyses of high voltage insulators under accelerated temperatures, and humidity. - First ever international standard and testing facility representing whole country environment (Pakistan) for accelerated aging analysis of up to 11 kV high voltage insulators (developed by Dr. Abraiz Khattak USPCASE, Funded by HEC-Pakistan).
- Variable accelerated sunlight degradation chamber for aging analysis of up to 11 kV high voltage insulators (developed by Dr. Abraiz Khattak USPCASE NUST Funded by HEC).


By developing this state of the art facility and specially running in combination with other already allied research laboratories at the center; USPCAS-E, NUST has become first and leading national platform of research and development in high voltage apparatus and systems.
It is pertinent to mention that NUST has highly skilled team in high voltage field which is capable to utilize High Voltage Laboratory NUST (HVLN) at maximum potential.
Keeping in view all the resources available, the high voltage team NUST aim is:
⇒ To collaborate with national power companies and industries with problems identifying and solving approach.
⇒ To conduct research and development aiming at meaningful development of products leading towards national and international commercialization.
⇒ To collaborate with international high voltage experts to get optimum results from the developed facility.
⇒ Produce quality graduates with high voltage expertise.
All relevant people from industry and academia are welcome to utilize this national facility.
References
- Khattak, Abraiz, et al. “Investigation of Hydrothermally Stressed Silicone Rubber/Silica Micro and Nanocomposite for the Coating High Voltage Insulation Applications.” Materials 14.13 (2021): 3567. DOI: 10.3390/ma14133567
- Khattak, Abraiz, et al. “Effects of Compression and Silica Addition on the Dielectric Properties of Epoxy Composites.” Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering 45.8 (2020): 6741-6750. DOI: 10.1007/s13369-020-04686-1
- Amin, M., Khattak, A., & Ali, M. (2018). Accelerated aging investigation of silicone rubber/silica composites for coating of high-voltage insulators. Electrical Engineering, 100(1), 217-230. DOI: 10.1007/s00202-016-0498-7
- Ryan, H. M. (Ed.). (2001). High voltage engineering and testing (No. 32). IET.
The author is an Assistant Professor at Department of Electrical Power Engineering, US-Pakistan Centre for Advanced Studies in Energy, National University of Sciences & Technology (NUST) and worked as Technical Lead in the development of High Voltage Laboratory, NUST. He can be reached via abraiz@uspcase.nust.edu.pk.
Author’s Research Profile: https://scholar.google.com/citations?hl=en&user=yLgtZzwAAAAJ&view_op=list_works