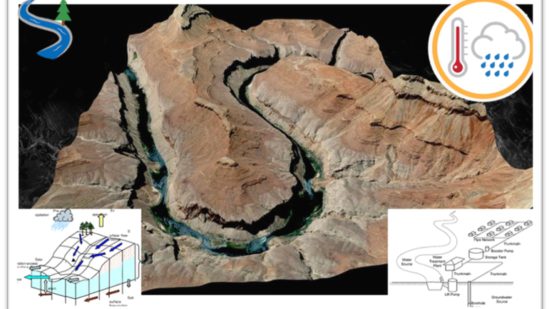
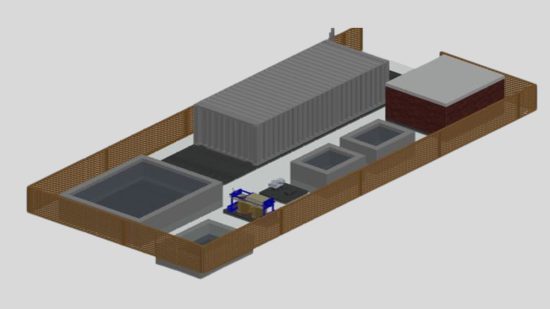
Building a Sustainable Future: Using Smart Materials to Combat Pakistan’s Energy Crisis
Pakistan’s climate, characterized by long, hot summers that stretch over eight months, poses a significant challenge for maintaining comfortable living environments. With over 50% of electricity consumption attributed to residential buildings and the energy demand rising at 4% annually, the reliance on air conditioning systems to cool buildings leads to skyrocketing energy demands. According to…
![]()